Robots require extensive information about their environment in order to function seamlessly and effectively. This information is collected by various sensors that allow the robot to see, feel and understand its surroundings. 3D sensors are some of the newly available –and increasingly less costly–sensors for robots that provide a rich three-dimensional understanding of their environment, allowing robots to be 'self-aware'.
Over the past decade, 3D sensors have undergone rapid development and are now being used in a number of different applications. They have become one of the most versatile and ubiquitous types of sensors that have found numerous applications in robotics – from map creation, combined assembly and inspection, surface and object inspection to object detection and collision avoidance.
Technological advances have led to smaller, more accurate, and easily configurable 3d sensing cameras that have dramatically increased robotic precision and reliability.
In this roundup, we will discuss the different types of 3D sensors, how they work, and some of the key applications of 3D sensors in robotics.
What Is A 3D Sensor?
A 3D sensor is a depth-sensing device that can measure the distance to, or the orientation of, an object in three dimensions. The three axes of measurement are typically the x, y, and z axes, which correspond to the left-right, forward-backward, and up-down directions, respectively. Ideally, 3D technology mimics the human visual system, which perceives the world in three dimensions.
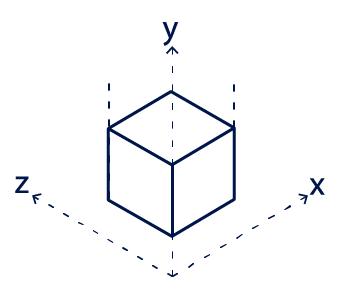
3D sensors can be classified into two categories according to how they measure distance: active and passive. Active 3D sensors use structured energy emission and detection, such as lasers, to measure distance.
On the other hand, passive sensors measure the distance to an object by analyzing the reflected light or radio waves. Passive sensors use the triangulation principle to recover depth information and calculate the distance between the object and the sensor.
How Do 3D Sensors Work?
3D sensors use various methods to measure distance. Active sensors emit structured light in the form of either laser or infrared radiation and then measure the time it takes for the light to return to the sensor.
On the other hand, passive sensors use reflected light or radio waves to measure distance. These sensors usually have a transmitter and receiver that are separated by a certain distance. The distance is then calculated by measuring the time for the signal to travel between the two devices and then back to the receiver.
In order to clearly understand how a 3D sensor works, let's take a look at an example of an active 3D sensor, the ultrasound range finder.
An ultrasound range finder emits a burst of ultrasonic sound waves and then measures the time it takes for the sound waves to return to the sensor. The time difference between the emission of the sound waves and their return is used to calculate the distance to the object.
The distance is then converted into a digital value that is processed by the 3D sensor's microcontroller. The processed data is then output as an electrical signal that can be used to create a three-dimensional image of the object.
Types of 3D Sensors
There are a number of different types of 3D sensors that are used in a variety of applications. The primary factors that determine 3D sensor selection include sensor performance, environmental limitations, and impact on the host. Here are some of the most common types of 3D sensors in the market today:
1. Stereo 3D Sensors
Stereo 3D sensors are the most common type of 3D sensor. These sensors are inexpensive and have an excellent overall performance.
Stereo 3D sensors usually consist of two cameras that are placed at a fixed distance apart. The cameras measure the distance to each object by analyzing the differences in the images captured by the two cameras. Stereo 3D sensors can either be active or passive and are used for surface inspection, object detection, and mapping.
2. Structured Light Sensors
Structured light sensors use lasers or infrared radiation to project a known pattern such as squares, dots, or lines onto an object's surface. The sensor then measures the distortion of the pattern caused by the object.
Next, the sensor uses the triangulation principle to calculate the depth and distance of the object based on the pattern distortion.
Structured light 3D sensors are typically used for industrial applications such as surface inspection, object detection, quality control, 3D printing, scanning, and measurement.
3. Time-of-Flight Sensors:
Time-of-Flight sensors are a type of LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensor that is used to measure distance. ToF sensors are the most accurate type of 3D sensor. These sensors use lasers to emit a burst of light to ascertain differences in object depth based upon measurable light variances.
They use a technique known as pulse-echo detection to measure an object's distance and depth. ToF creates a 3D point cloud of X, Y, Z coordinates to map the object based on the time difference between the emission of the light and its reflection back to the sensor.
ToF sensors are typically used in industrial and medical applications such as machine vision, 3D scanning, motion tracking, indoor navigation, gesture recognition, and biometric identification.
Applications of 3D Sensors in Robotics
The use of sensors for robots is constantly increasing with the advent of new and innovative technologies. Some of the most common applications of 3D sensors in robotics are discussed below.
· Navigation
3D sensors are used in navigation systems to help robots locate and track their position in relation to their environment. 3D sensors are used to calculate the distance between the robot and its surroundings, which is then used to create a map of the environment, helping them navigate and detect obstacles.
· Motion Tracking
3D sensors are also used in motion tracking systems to track the movement of robots and other objects in relation to each other. This is used to help control the movement of the robots and ensure that they collaborate seamlessly and remain in sync with each other.
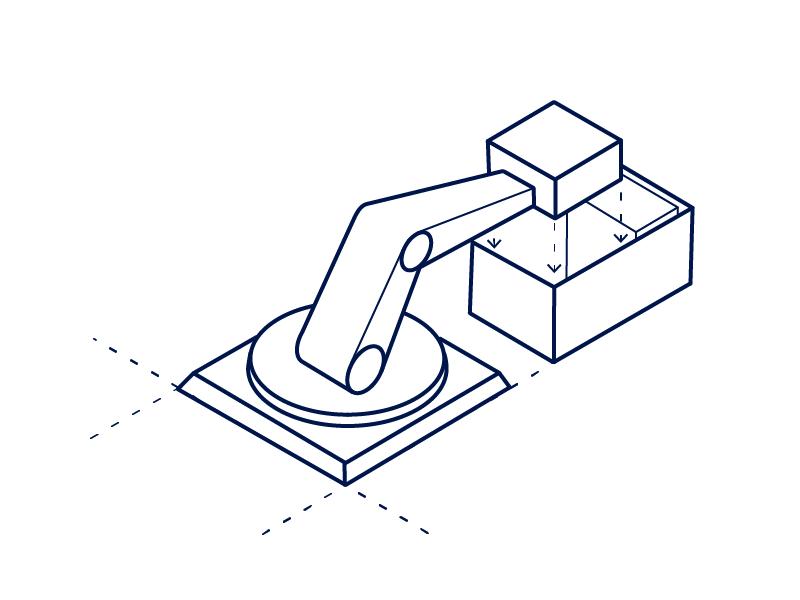
· Object Detection
3D sensors are also used for object detection, which is the process of identifying and locating objects within their range. Robots use this to identify and track objects in their environment, which can be used for tasks such as collision avoidance or picking up objects.
· Depalletizing and Palletizing
In manufacturing, distribution, and fulfillment applications, 3D sensors are also being used in depalletizing and palletizing systems to detect and locate objects. Depalletizing is the process of removing objects from a pallet while palletizing is the process of placing objects on a pallet.
3D sensors are used to create a three-dimensional model of an object using its silhouette. This is used to help the robot understand the object's shape and determine the best way to place it on a pallet for storage and transport. Companies such as Mech Mind are creating intelligent depalletizing and palletizing robotic solutions using 3D sensing, deep learning, and AI to improve accuracy and speed.
Benefits of Using 3D Sensing Cameras in Robotics
The use of 3D sensors is becoming increasingly common in various industries and applications, and their use in robotics is no exception. 3D sensors offer a wide range of benefits that can improve the performance and functionality of robots. Some of the key benefits include:
· Saves time and money: 3D sensors help automate processes and improve accuracy, which can lead to faster and more efficient operations.
· Improved safety: The use of 3D sensors in robotics can also enhance safety by helping to avoid collisions and accidents.
· Enhanced performance: 3D sensors can help robots perform better in difficult or hazardous environments, such as those that are dark, hot, dusty, or wet.
· Greater flexibility: 3D sensors allow robots to move and operate in areas that are not accessible to traditional sensors.
· Easier integration: 3D sensors are easier to integrate into robots, making it simpler and faster to get them up and running.
· Lower cost: 3D sensors are becoming increasingly more affordable, making them an economical option for many applications.
· Increased accuracy: 3D sensors offer greater accuracy than traditional sensors, improving the quality and precision of tasks performed by robots.
Wrapping It Up
3D sensors are revolutionizing robotics by making it possible to create robots that can interact with their environment in a more natural and intuitive way. These sensors are helping to create more intelligent and more versatile robots that can be used for various purposes such as navigation, object detection, motion tracking, security and surveillance, and medical applications, among others.
3D sensor technology is constantly evolving and becoming more sophisticated, which is sure to pave the way for even more innovative applications in the future. So far, 3D sensors have shown immense potential in robotics, delivering unique advancements in the way day-to-day activities are perceived and approached. It will be exciting to see what the future holds for 3D sensors and robotics.