In January 2026, the World Economic Forum (WEF) Annual Meeting in Davos once again put advanced manufacturing in the global spotlight. In recent years, a clear message has become increasingly apparent: manufacturing competitiveness is no longer defined by scale alone, but also by intelligence, adaptability, and resilience. With its flagship program recognizing the world’s most advanced factories, the WEF’s Global Lighthouse Network continues to showcase how AI, data, and digital technologies are transforming production at scale.

As manufacturers set their 2026 automation goals, these Lighthouse Factories provide a practical blueprint. Across industries, a clear pattern emerges: advanced automation is driven not by a single breakthrough, but by the integration of sensing, intelligence, and action. Within this stack, 3D vision has quietly become a foundational capability, enabling robots to perceive the physical world with depth, accuracy, and context. Mech-Mind brings this stack together with an industry-leading portfolio of industrial 3D cameras (“Eye”), AI software suites (“Brain”), and dexterous hands (“Hand”), empowering partners and system integrators to tackle demanding industrial robotic applications.
From 3D Vision to Physical AI
According to the WEF Global Lighthouse Network, AI is now deployed in over 220 factories worldwide, driving measurable impact across production and supply chains. The distinction of these leaders lies not in experimentation, but in execution. They embed intelligence directly into production workflows, enabling systems to sense conditions, adapt in real time, and continuously improve.
In practice, this transformation drives the evolution from isolated automation cells to data-rich, flexible production units. AI rarely works alone. Successful transformations typically integrate multiple technologies, including AI models, edge computing, IoT, and advanced sensing, into closed-loop systems. Within these loops, 3D vision systems act as the “eyes,” delivering real-time data to AI-driven decision engines that guide robots and processes. Achieving ambitious 2026 targets of higher mix, tighter tolerances, and zero-defect quality requires this level of perception.
Why 3D Vision Enables Flexible Manufacturing
Modern production is defined by variability: product variants change frequently, parts arrive in unpredictable orientations, and customization has become the norm. 3D vision addresses these challenges by providing a complete spatial understanding of every object and scene.
Adaptive robot guidance is one clear example. With 3D vision, robots can locate and grasp parts in any position or orientation, supporting reliable bin picking, mixed-model assembly, and rapid changeovers. One robot can handle multiple SKUs on the same line without customized fixtures, significantly reducing downtime.
3D vision is also characterized by reliable accuracy. 3D vision allows robots to perceive geometry and spatial relationships precisely in real time, allowing automation systems to maintain consistency across tasks such as picking, assembly, and intralogistics, reducing errors while ensuring repeatable performance at industrial scale.
Safer and more effective coordination between humans and robots is another key advantage of 3D vision. By equipping robots with reliable spatial perception, this technology fosters a more secure and adaptable production environment, unlocking new levels of operational flexibility and productivity.
Together, these capabilities make flexible, high-mix production commercially viable. Factories no longer need to choose between efficiency and customization—3D vision delivers both. Backed by real-world application cases across diverse industries, Mech-Mind’s 3D vision system delivers high performance, proving adaptability and reliability.

3D vision-guided case examples
Why 3D Vision Enhances Quality Control
Lighthouse Factories are increasingly moving from sampling-based quality control to full-process, inline inspection. Rather than checking a small percentage of parts, advanced plants now inspect every component in real time.
An AI-powered 3D vision system makes this possible. High-precision 3D cameras capture precise geometric data at production speed, immediately flagging deviations and feeding results back to upstream processes so defects are caught early and prevented from propagating downstream.
The impact is significant. Manufacturers adopting automated 3D inspection report substantial reductions in inspection costs and rework, with first-pass yield often approaching or exceeding 99.8%. More importantly, it elevates quality control to a new level of predictability, repeatability, and data-driven insight.
Equally critical is the data traceability. Each inspection result is linked to time, station, and part identity, allowing engineers to trace issues to their root cause in minutes rather than days. Achieving zero-defect production requires this level of visibility.
The Mech-Mind 3D Inline Measurement System delivers high-precision dimensional inspection of key features on industrial parts, sub-assemblies, and more. The system provides industry-leading accuracy, high-speed measurement, real-time inline inspection, full-process data traceability, thermal drift compensation, and flexible adaptability.
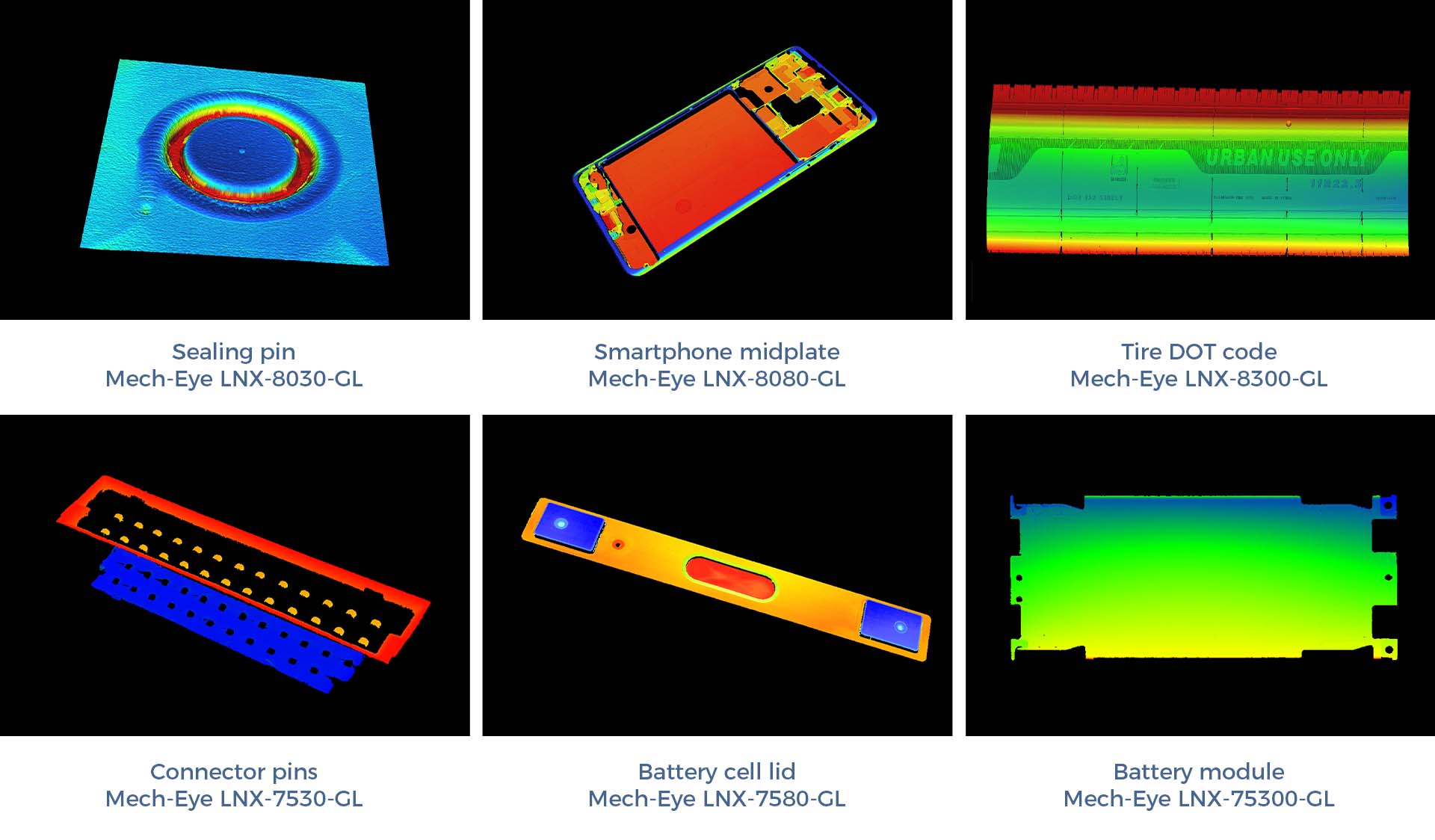
Point cloud examples (color rendered by height)
From Seeing to Understanding: Embodied Intelligence
As vision capabilities mature, the next frontier lies in intelligence that is easier to deploy and scale. Leading manufacturers are now exploring embodied AI systems that combine perception, reasoning, and action in a unified framework.
One emerging approach is natural-language interaction with robots. By combining 3D vision with multimodal AI models, robots can interpret human instructions in context. Instead of programming, operators can describe tasks in natural language, and the system executes them correctly using visual understanding. Mech-Mind’s multimodal large model Mech-GPT allows robots to interpret natural-language commands and perceive complex environments, significantly lowering the barrier to use.
This “Eye–Brain–Hand” model represents a shift in how automation is deployed. Vision provides perception, large models provide reasoning, and robots provide physical execution. Together, the model lowers the barrier to automation and makes advanced systems accessible to a wider range of users.
Independently developed by Mech-Mind, the general-purpose robot “Eye-Brain-Hand” portfolio offers powerful perception, understanding, and manipulation capabilities, and is adaptable to diverse robot forms and application scenarios.

3D Vision’s Role in 2026 Industrial Automation
The factories leading industrial transformation are those that deeply integrate intelligence into their operations. 3D vision has become a cornerstone of this integration—enabling flexible production, inline quality, and intelligent logistics at scale.
For manufacturers planning their next phase of automation, the implication is straightforward. 3D vision is no longer a niche add-on or a pilot technology. It has become a foundational layer of modern manufacturing systems, supporting efficiency, resilience, and long-term competitiveness.
As more factories advance toward Lighthouse status, 3D vision will play an increasingly important role. By giving robots reliable perception and actionable insight, manufacturers can turn ambitious 2026 goals into operational reality—transforming factory floors into global benchmarks of industrial excellence.
As a pioneer in 3D vision and embodied intelligence, Mech-Mind is working with global manufacturers and system integrators to turn this vision into reality—bringing intelligent perception to factory floors at scale.